Bias-variance dilemma (Geman et al., 1992). It can be demonstrated that the mean square value of the estimation error between the function to be modelled and the neural network consists of the sum of the (squared) bias and variance. With a neural network using a training set of fixed size, a small bias can only be achieved with a large variance (Haykin, 1994). This dilemma can be circumvented if the training set is made very large, but if the total amount of data is limited, this may not be possible.
Latest Updates: error RSS
-
Arif
-
Arif
Stone 1974 is referenced in:
Michaelsen J. 1987. Cross-validation in statistical climate forecast models. J Climate Applied Meteorology, 26:1589-16001520-0450(1987)026-1589-cviscf-2.0.co;2.pdfSet
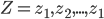 consists of predictions and targets
consists of predictions and targets 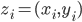
A set of prediction rule
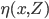 will be used to predict y0 from
will be used to predict y0 from 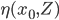
Let
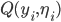 be the accuracy.
be the accuracy.
by least squares this will usually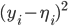
in other words expected Err is
![Err= E[Q(y_{i},\eta(x_{0},Z))]](http://lakm.us/thesit/wp-content/uploads/eq_a3a3253210769351b42ecc2c29b07f59.png)
MSE
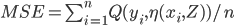
In cross validation
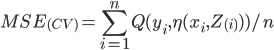
-
Arif
If we assume a normally distributed population with mean μ and standard deviation σ, and take sample
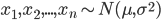
statistical error is then
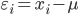
Residual
while residual is
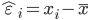
hat over the letter ε indicates an observable estimate of an unobservable quantity called ε.